Understanding Reverse Osmosis (RO). How RO Systems Work and What They Do.
1. Why Choose Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration System?
Fresh Delicious Water
RO filtration improves the taste and appearance of water and eliminates odour by removing all the chemicals, debris and contaminants that cause such problems.
Save your money
With an RO system, you will no longer need to arrange for delivery service and stop purchasing bottled water altogether. You will always have premium quality freshwater within reach for just pennies per gallon.
Easy Maintenance
With very few parts to be replaced, maintenance and cleaning of RO systems is a simple task.
Removes Impurities
RO systems remove pollutants from water including nitrates, pesticides, sulfates, fluoride, bacteria, pharmaceuticals, arsenic to name a few. The Carbon filter also removes chlorine and chloramines.
Top Residential RO Sellers:
Installed at the kitchen sink:
An RO filtration system is installed at a single water connection and thus is called a point of use (POU) water filtration system. It can be installed on a wall or inside the cabinet under the kitchen sink. It can also be connected to the fridge and/or ice machine.
2. How Does Reverse Osmosis Work?
Reverse Osmosis is essentially a simple Water Filtration Process in which dissolved inorganic solids and impurities are removed from a solution, ie water.
This is accomplished by household water pressure pushing the tap water through a thin semi-permeable membrane with small pores that only pure water can pass through, while larger particles such as impurities and bacteria are rejected.
A few impurities Reverse Osmosis filtration technology can remove:
- Fluoride
- Lead
- Chlorine
- Chlormamine
- Pesticides
- Detergents
- Nitrates & Sulfates
What about the Contaminants That Don’t Pass Through the Semi-permeable Membrane?
Ro systems incorporate 5, 6 or 7 stages including the semi-permeable RO membrane. When water from your household main line is pushed under pressure through all the stages, the impurities are filtered out and flushed down the drain. Leaving clean and fresh drinkable water in the tank for your use.
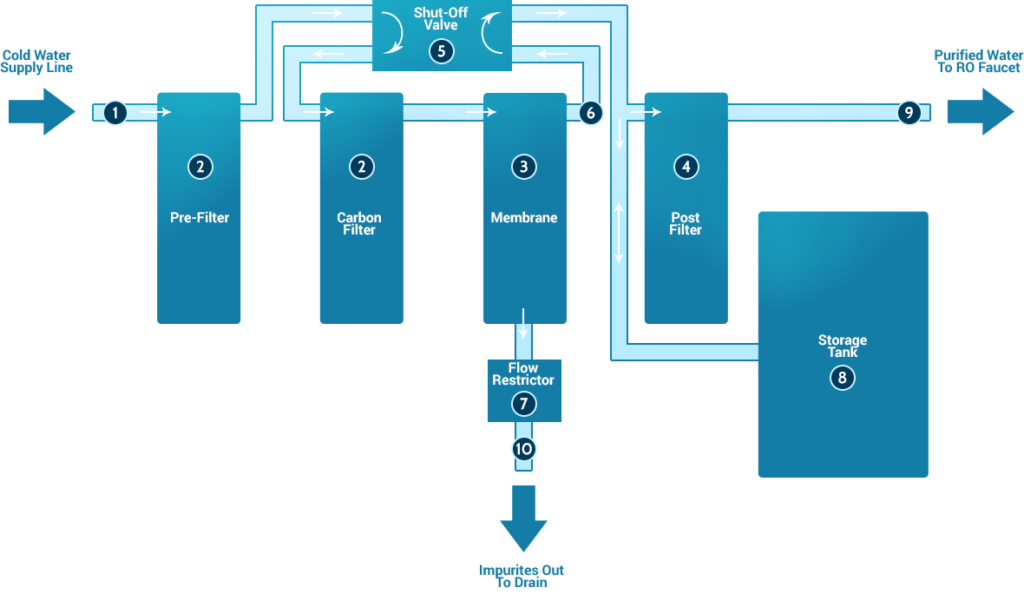
What are generally the main components of a Reverse Osmosis System?
Note that although most RO systems look similar and work basically the same way, they differ in the QUALITY of their components.
- Cold Water Line Valve: This valve is fitted onto the cold-water supply line on one side and has a tube on the other side that attaches to the inlet side of the RO system prefilters. This is the connection with a water source for the RO system.
- Pre-filtration: Water from the cold-water supply line enters the Reverse Osmosis system Pre-Filters. There’s typically more than one pre-filter used in a Reverse Osmosis system. The most commonly used are sediment and carbon filters. These pre-filters are used to remove sand, dirt, and other sediments that whereas carbon filters are used to remove chlorine. These filters can be perceived as the army protecting the System from impurities that may clog it and/or chlorine which can damage the membrane.
- Reverse Osmosis Membrane: The Reverse Osmosis Semi-Permeable Osmotic membrane is the core of the RO system. It is a barrier for a variety of organic and non-organic contaminants dissolved in water, heavy metals, radioactive and carcinogenic elements. It only allows water in, as its porosity is the size of water particles, that is 0,0001 micrometers.
- Post-filtration: When the treated water leaves the pressurized RO tank, it goes through the final stage which is the Postfilter(s); right before it reaches the RO faucet. This consists of Granular Activated Carbon filter(s) to remove any remaining taste or odour. A 6-stage RO system would include a mineralizer cartridge to dissolute water and in turn, improves the taste and smell of water.
- Automatic Shut Off Valve (SOV): The RO system has an automatic shut off valve to conserve electricity and water. This valve automatically closes when the storage tank is full to stop water from flowing through the membrane and down the drain. Once the RO faucet is switched on and water flows out, the pressure in the tank drops causing the shut-off valve to open in order to allow the purified drinking water to flow through the RO membrane while the wastewater is diverted towards the drain.
7. Flow Restrictor: Located in the Ro drain tubing; the main purpose of the flow restrictor is to regulate the flowing water in order
to maintain the flow rate required to obtain premium quality drinking water. It also helps to maintain pressure on the inlet side of the
membrane to force more water to flow into the membrane and thus get treated
8. RO Storage Tank: Treated water leaves the Osmotic membrane go into a pressurized storage tank. The standard RO storage tank holds from 2-4 gallons of water and has a bladder to keep the water pressurized
9. Faucet: The RO system comes with its own faucet, which is usually installed on the kitchen sink.
10.Drain line: This is a tube that runs from the outlet end of the Reverse Osmosis membrane housing down to the drain, disposing of the
wastewater containing impurities and contaminants that have been filtered out.
2. How Does Reverse Osmosis Work?
There Are Generally Four Stages In The Reverse Osmosis Process: There are 4 main stages in the Reverse Osmosis Process:
FIRST STAGE: SEDIMENT FILTER:
Designed to strain out sediment, silt, and dirt and has a double purpose as it not only filters out sediments but also prevents dirt from getting to the delicate RO membranes which can damage it.
SECOND STAGE: CARBON FILTER:
Designed to remove chlorine, poisonous compounds, organic/ mechanical impurities and other contaminants that affect the performance and lifespan of the RO membrane as well as improve the taste and odour of your water.
THIRD STAGE: REVERSE OSMOSIS MEMBRANE:
Designed to allow only water molecules through (0.0001 micrometers); filtering out almost any contaminants
FOURTH STAGE: POST- FILTER (ALSO KNOWN AS POLISHING FILTERS):
The final post filter (carbon filter) improves taste and odor in the water to ensures that you’ll have optimum quality drinking water.


